Architecting Modern Data Platforms
Data Architecture Principles
Whether you are responsible for data, systems or application architecture, you need to define some principles to help you navigate the fast-paced modern world. Data Architecture Principles are the foundation for data architecture that will allow your business to run at an optimized level today, and into the future.
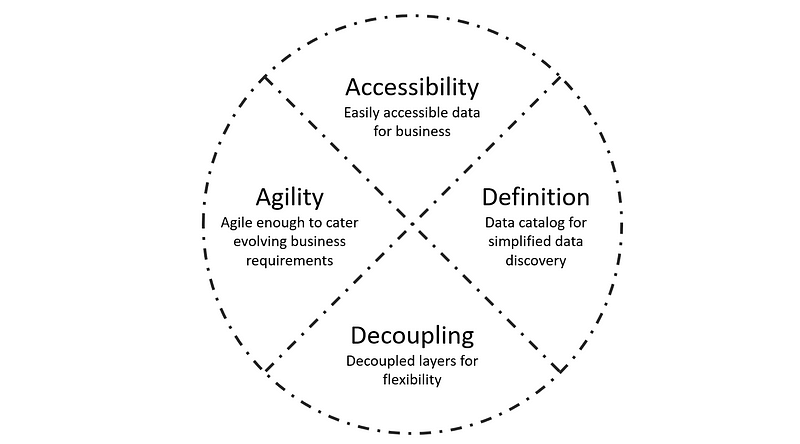
Adhere to ADDA (Accessibility, Definition, Decoupling, Agility)
-
Data Accessibility is critical for the success of any business. Easily accessible data enables you to move quickly, focus on the product, and build a data-informed pipeline where data leads to better decisions and actions.
-
Data Definition or Catalog helps analysts and other data users to find the data that they need, serves as an inventory of available data, and provides information to evaluate fitness data for intended uses.
-
Data Decoupling helps in design since it allows each data layer to be independent of other data layers.
-
Data Agility is when your data can move at the speed of your business. For companies to achieve true data agility, they need to be able to access the data they need, when and where they need it.
So the first data architecture principle is to make sure that business data is accessible, defined, decoupled and agile.
Design for RSM (Reliability, Scalability, Maintainability)
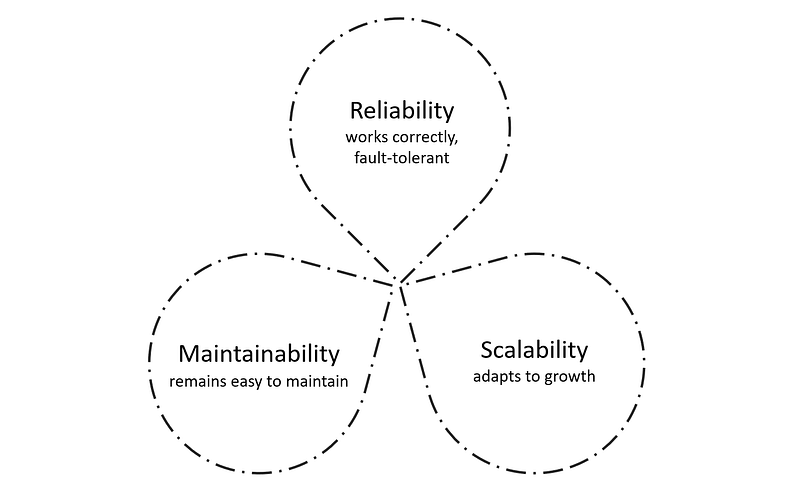
- Reliability means the data systems we are designing work correctly and fault-tolerant up to some level.
- Scalability means data systems are adaptable to growth in a linear way.
- Maintainability means that data systems remain easier to maintain.
Second data architecture principle is that the data systems remain reliable, scalable and maintainable over time.
Use Right Tools
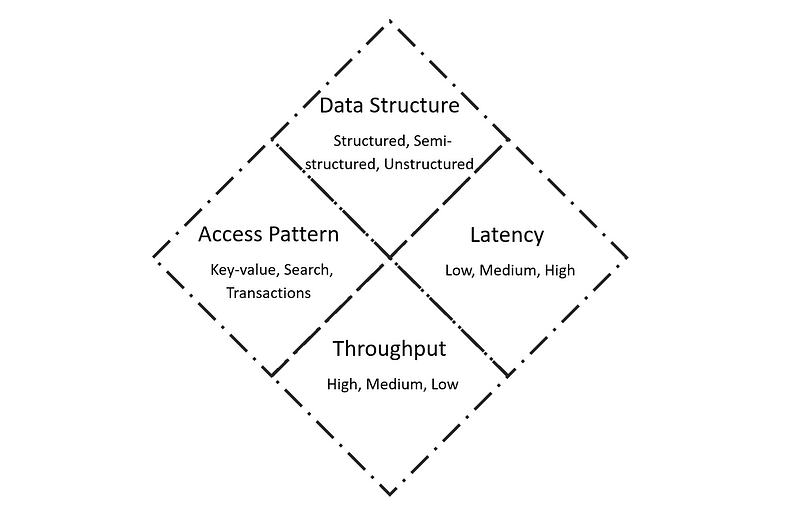
We need to use the right tool at each data layer by aligning the choice to the data structure, latency and throughput requirements and access patterns.
Cloud-Native/Agnostic
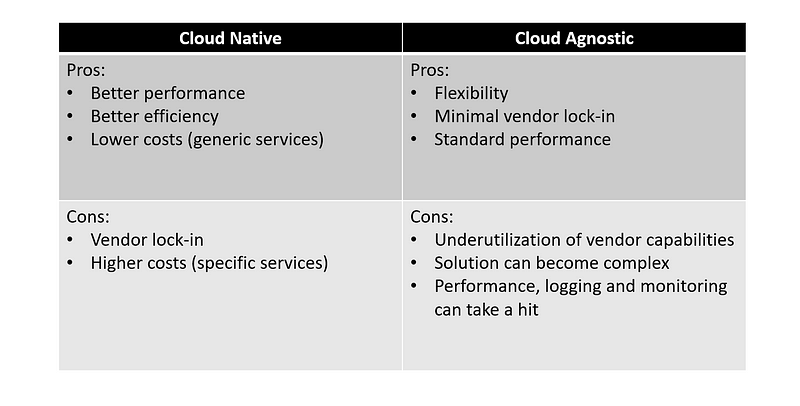 Whether you have the data on-premise or you are using single/multiple cloud service providers, each decision has its own pros & cons.
Whether you have the data on-premise or you are using single/multiple cloud service providers, each decision has its own pros & cons.
Be Cost-Conscious
Cost of building complex and ever-evolving data systems can be huge, we need to make sure we use available resources efficiently.
- Efficient consumption of services
- Select cost-conscious options
- Enforce policies and controls
Data Lake Basics
Data Lake is becoming the defacto standard in modern data platforms, let’s have a look at what it is and how it helps to build modern data systems.
Data Lake Definition
- An architectural approach
- Massive heterogeneous data stored centrally
- Available to the diverse group of users
- To be categorized, processed, analyzed & consumed
Data Lake Characteristics
- Structured, semi-structured & unstructured data
- Scaled out as required
- The diverse set of storage, analytics and ML/AI tools
- Designed for low-cost storage and analytics
High-Level Architecture
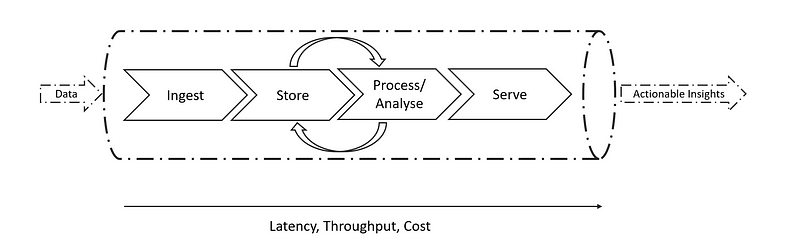
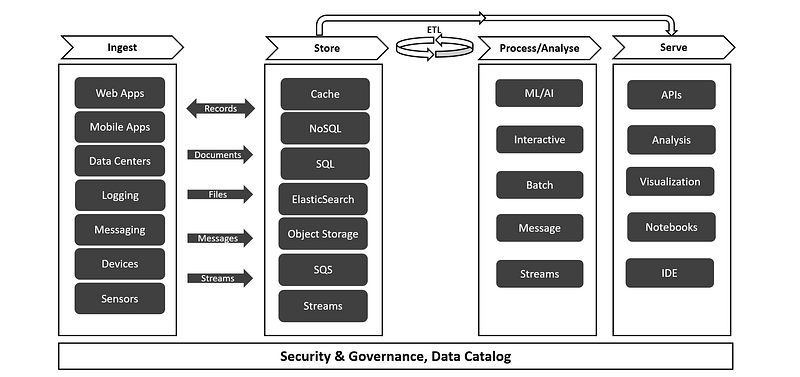
A typical data analytics platform takes business raw data as input and provides actionable insights. It has four layers: ingest, store, process/analyse & serve. Let’s have a look at each data layer in detail:
Data Characteristics
Ingest
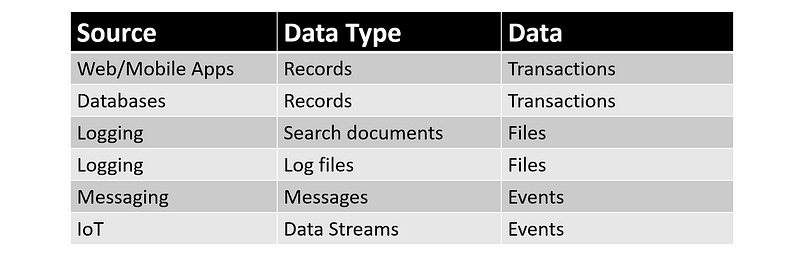
- Data can be ingested from a variety of data sources like web/mobile apps, databases, application logging, messaging and IOT devices.
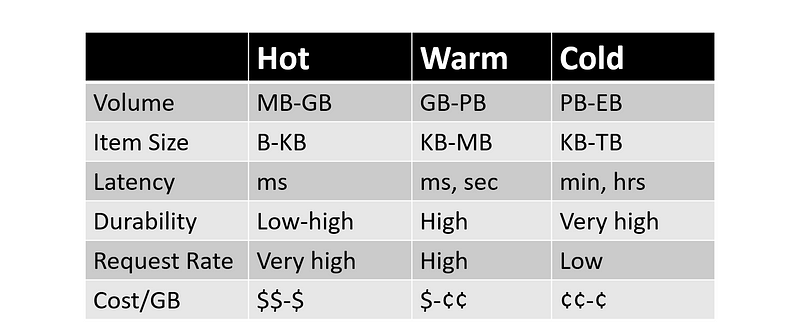
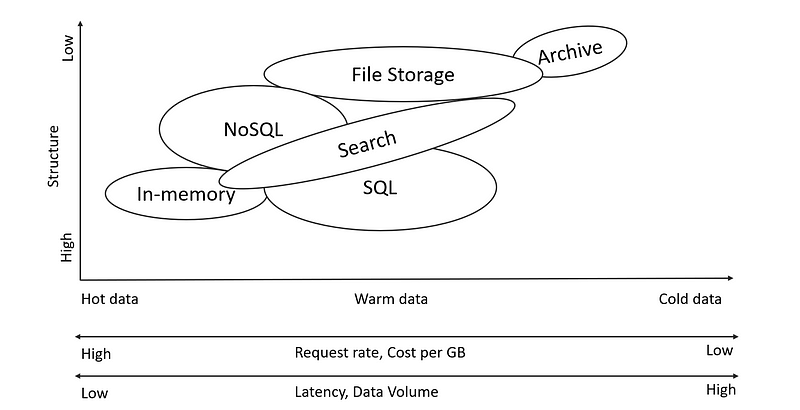
- Data can be hot, warm or cold based on its velocity, request rates and latency requirements:
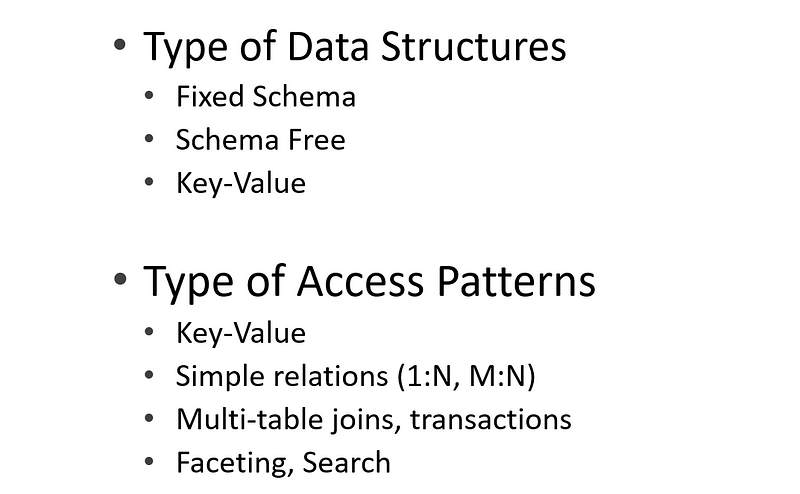
- Data can be categorized based on data structures and access-pattern requirements. Based on these characteristics, we decide how to store and process each type of data.
Storage
- How we are going to store data depends mainly on two major factors:
- What is the structure of the data?
- What is the frequency and usage of data?
Analytics Types
There can be different kind of analytics you may need to perform based on the structure and access-patterns of data.
- Message/Stream Analysis
- Interactive Analysis
- Batch Analysis
- Machine Learning/AI
- ETL Processing
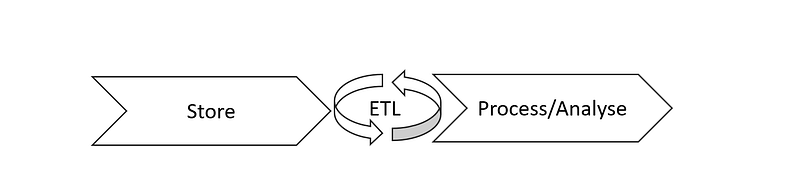
Store and Process/Analyse steps can be performed iteratively as after processing or analysing the results, you may need to store data in the processed form before acting further.
Serve
There may be various ways of serving insights to end-user (business, data scientists or developers).
- Applications & APIs
- Analysis & Visualization
- Notebooks
- IDEs
Putting It All Together
Now let’s combine what we have discussed till now, you may notice that ‘Security and Governance’ process needs to be applied across the data layers along with Data Catalog.
Product-Driven Data Architecture
While data lake is the defacto standard these days, still there are few issues that are to be addressed like ubiquitous data and source proliferation, innovation agenda and consumer proliferation, coupled pipeline decomposition.
Recently, Zhamak Dehghani has proposed a data architecture to move beyond a monolithic data lake to a distributed data mesh which can possibly address above mentioned concerns.
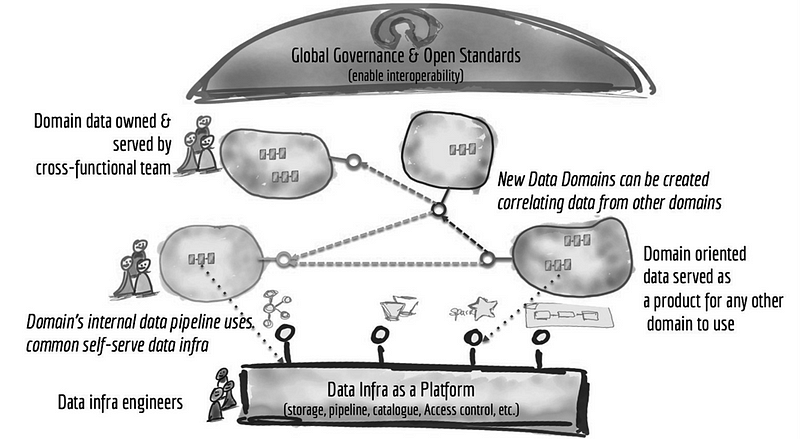 https://martinfowler.com/articles/data-monolith-to-mesh.html
https://martinfowler.com/articles/data-monolith-to-mesh.html
Reference Architecture
Before signing off, let’s also have a look at reference data architecture from leading cloud services providers like Azure, AWS and GCP.
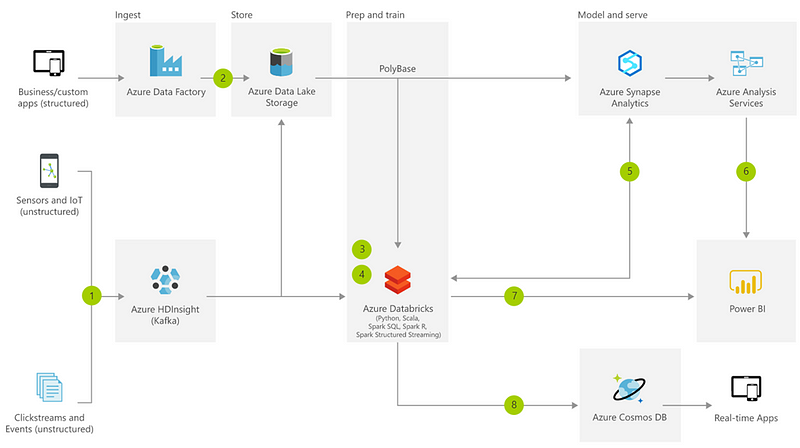
Reference Architecture — Azure
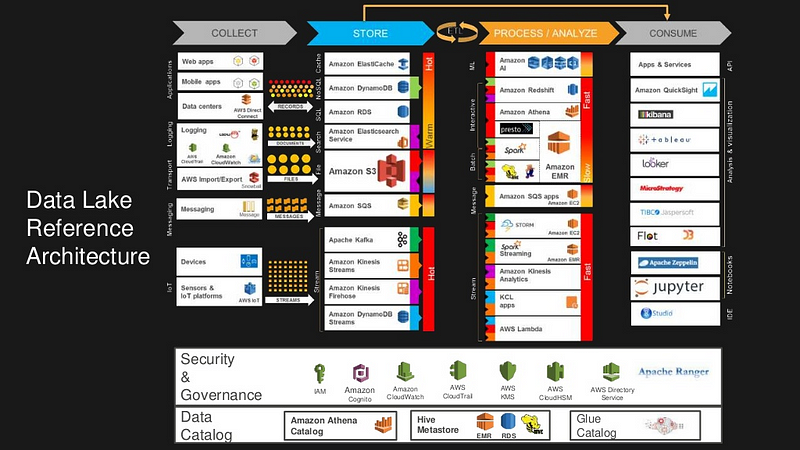
Reference Architecture — AWS
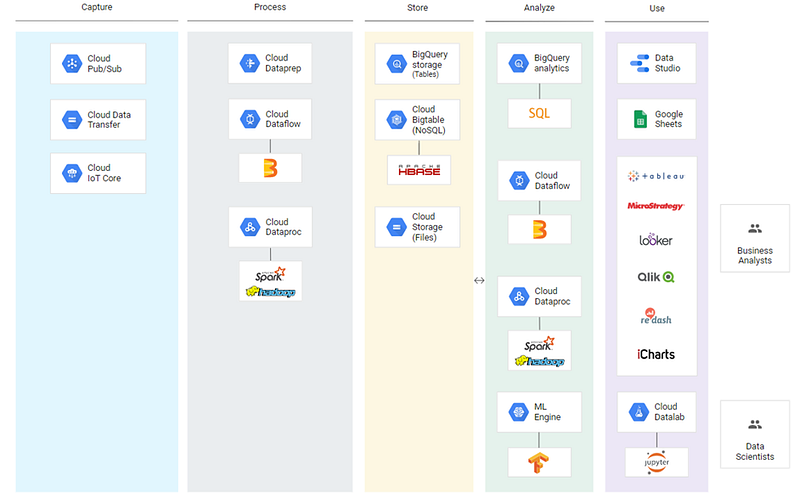
Reference Architecture — GCP
I hope you find this post useful, stay tuned for more, any feedback would be highly appreciated.
Ankit Rathi is an AI architect, published author & well-known speaker. His interest lies primarily in building end-to-end AI applications/products following best practices of Data Engineering and Architecture.
Why don’t you connect with Ankit on YouTube, Twitter, LinkedIn or Instagram?
If you have any questions or comments, click the "Go To Discussion" button below!